Castle Engine and Castle Studio
Castle is a platform for AI in closed environments.
It is implemented with a Spring AI backend, called Castle Engine, and a Vue frontend, called Castle Studio.
Since Castle is REST-based and using OAuth 2.0, Vue commponents can be copied and modified, and used in other applications with the same backend.
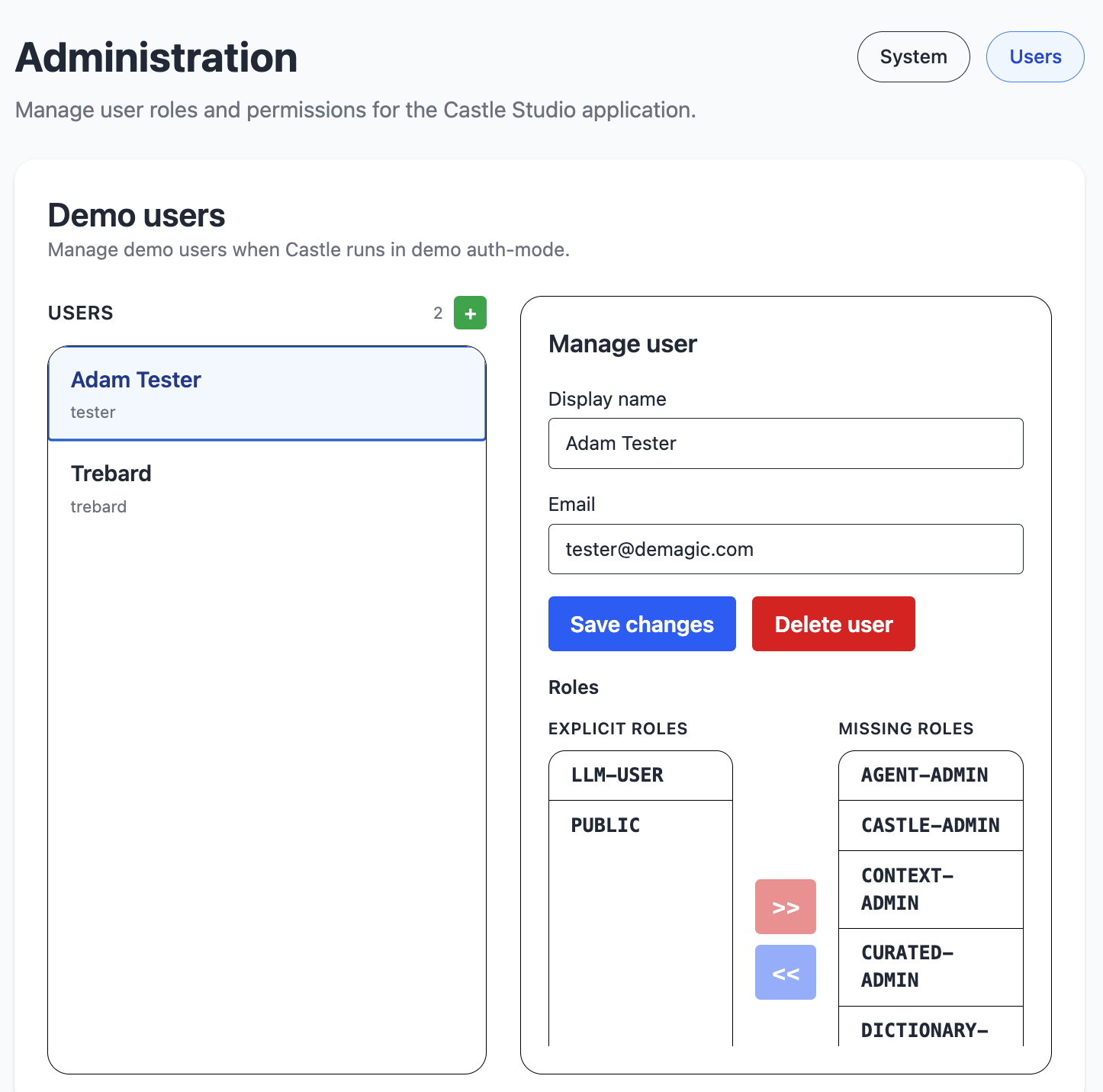
Roles
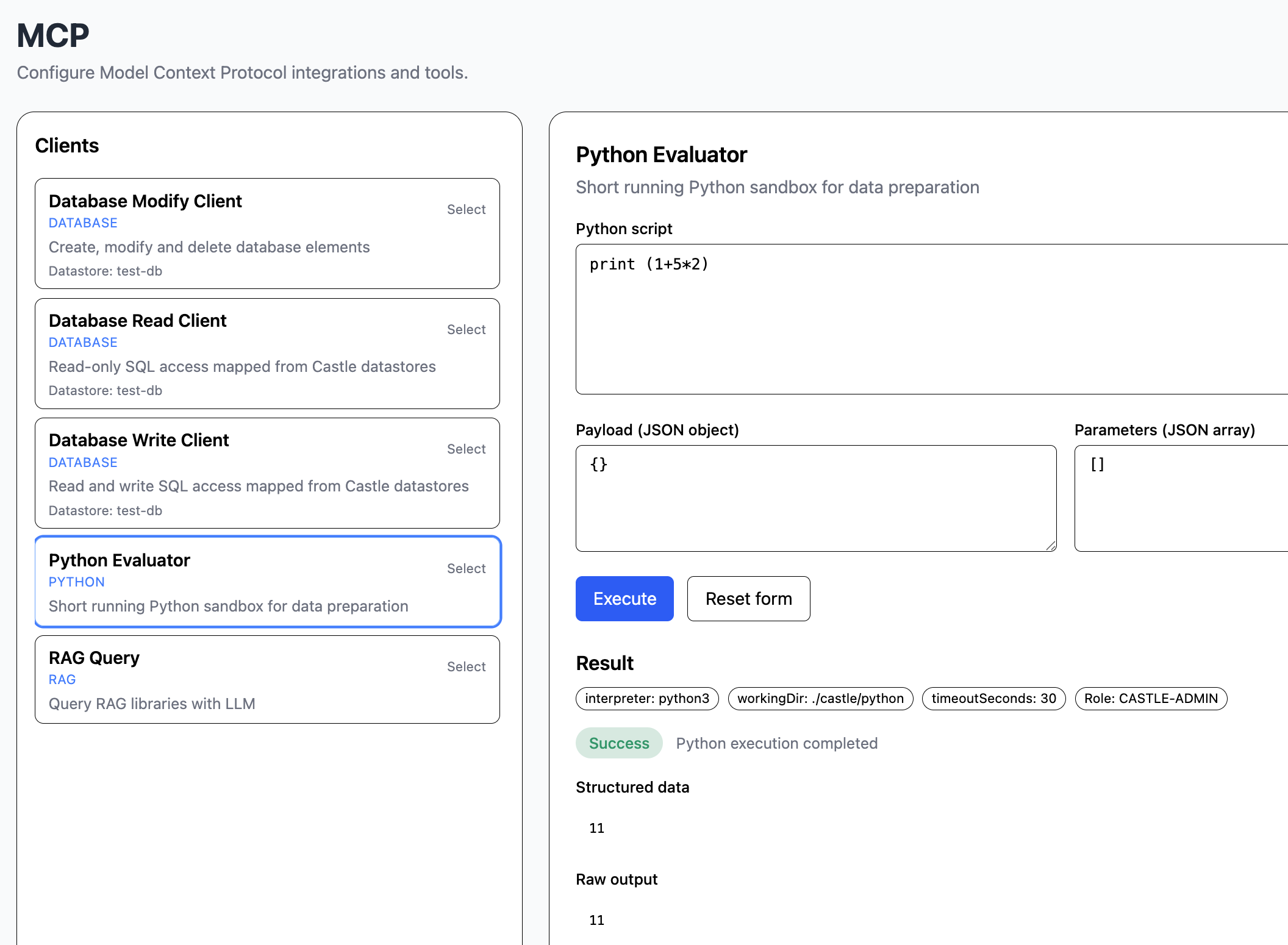
Castle uses a role system similar to Snowflake, where you can limit tool and data access using role assignments. You can map external roles, e.g. from OAuth 2.0, to Castle roles.
In the frontend, you select which role you want to use to execute a server request. This role is used for all access in the backend, so it is easy to simulate access restrictions by simply selecting a role with less or other access rights.
Most menu elements in the frontend requires a selected role or a child of the selected role.
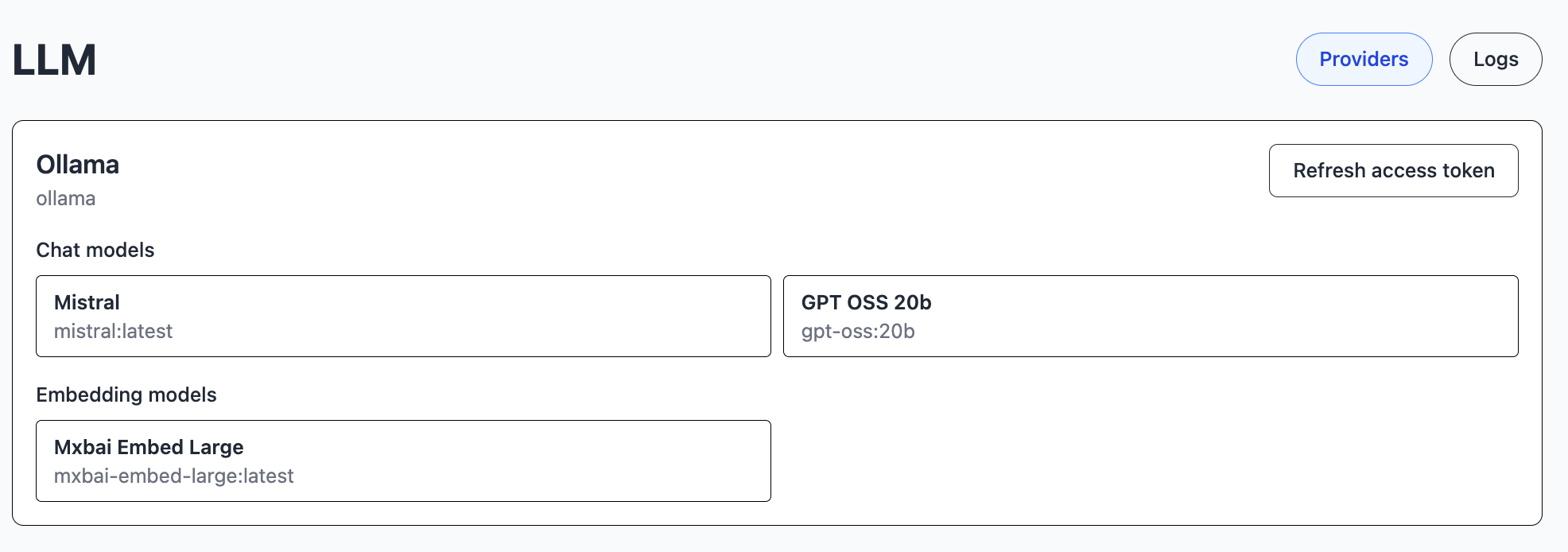
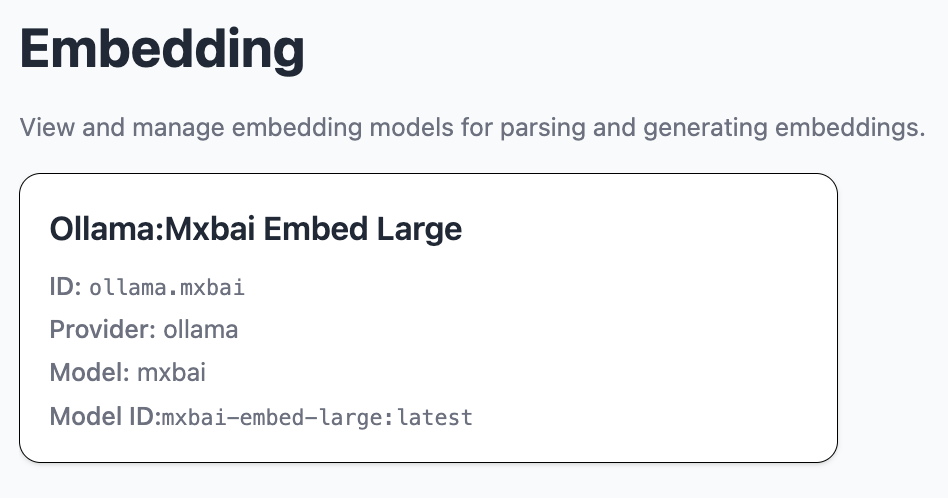
LLM
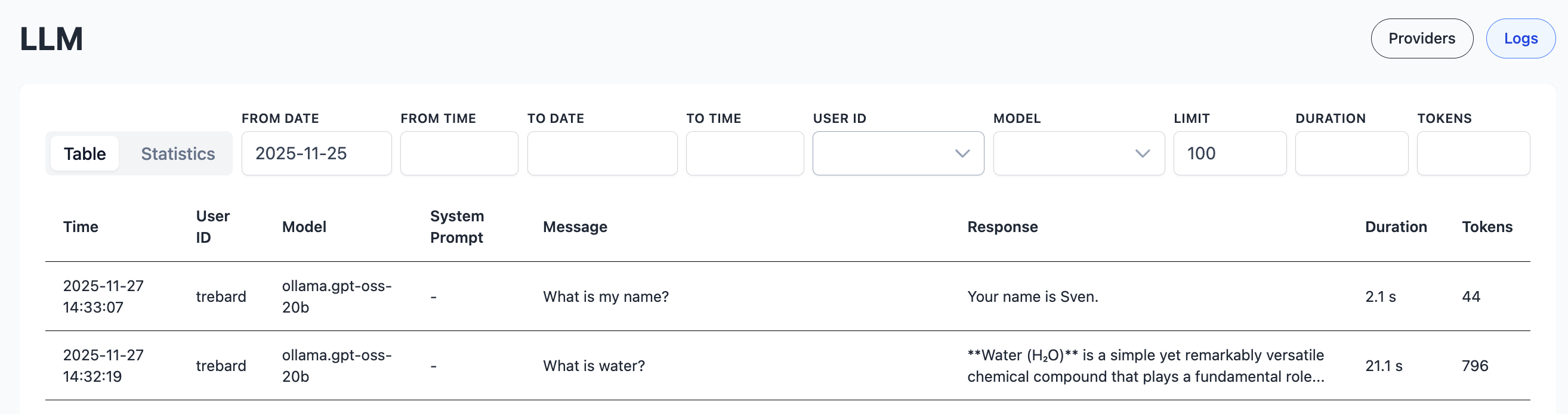
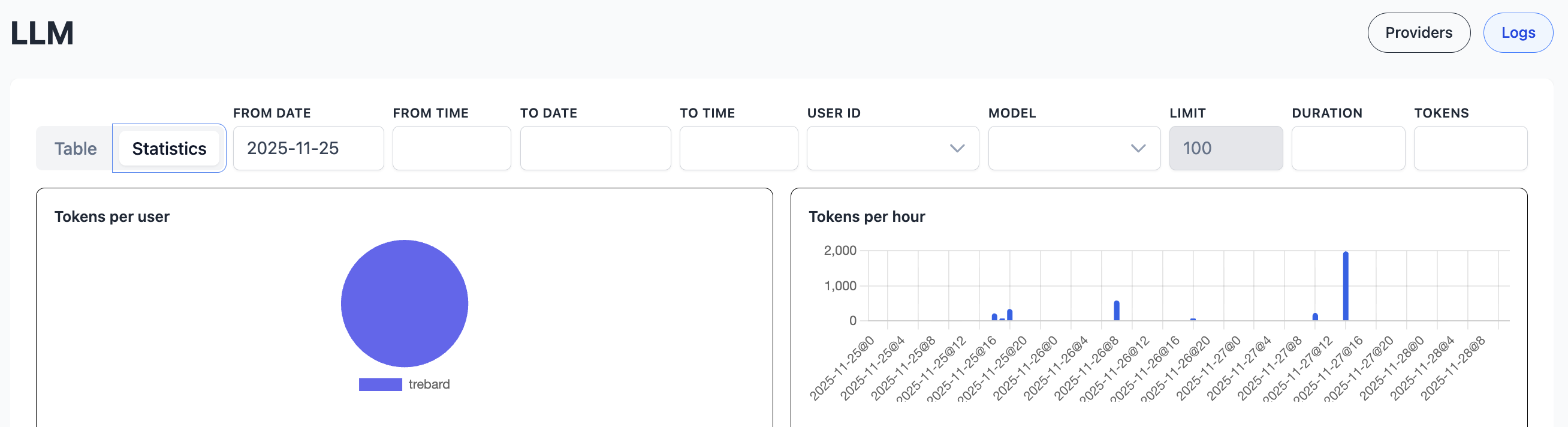
The llm (large language model) module is used for handling and displaying llms. The llms are defined in the application properties. The llm service keeps track of llm token usage for individual users.
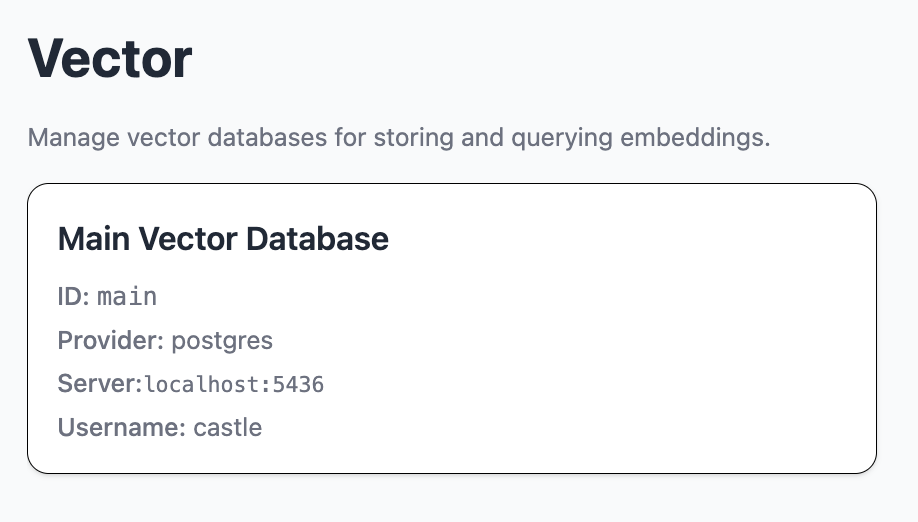
Datastore
The datastore module is used for handling and displaying datastores.
A datastore is the location of data. It may be a local catalog, a database or a website.
An asset is a document in a datastore. It may be a file, a database table or a webpage.
The datastores are defined in the application properties, to avoid credential handling in the frontend.
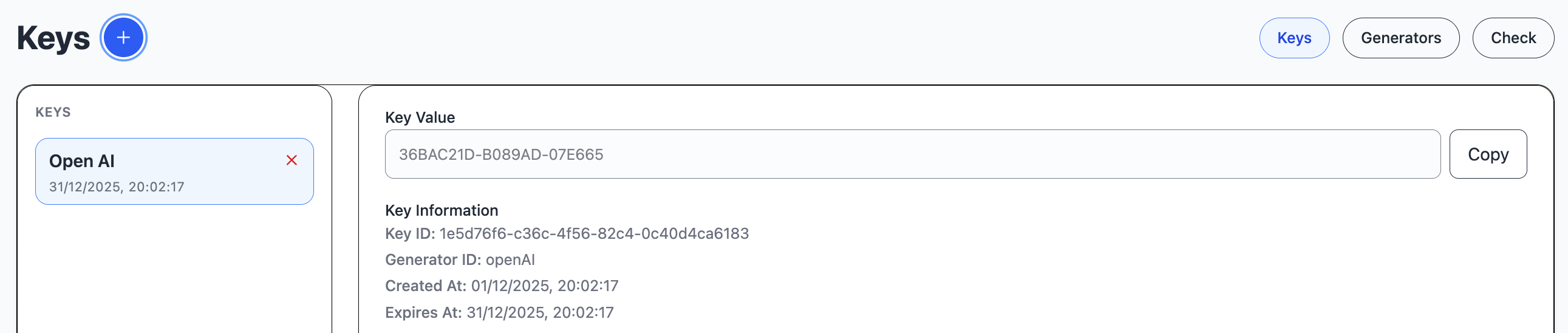
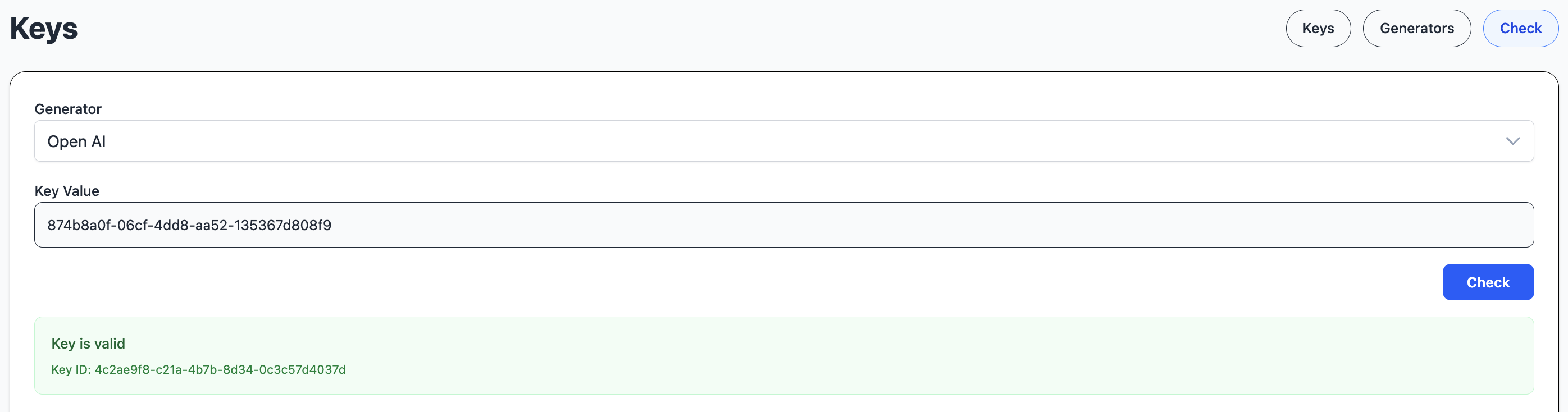
Keys
A key generator defines how to generate and hash a key.
A pattern is a number of pattern keys, each followed by an optional count.
Keys:
- "a": a-z
- "A": A-Z
- "x": 0-f
- "X": 0-F
- "d": digit 0-9
- other characters are just copied into the pattern
For instance, "X8-X6-X6" may result in key value "2F8A342C-3135E4-BA5F4F"
Translation
RAG
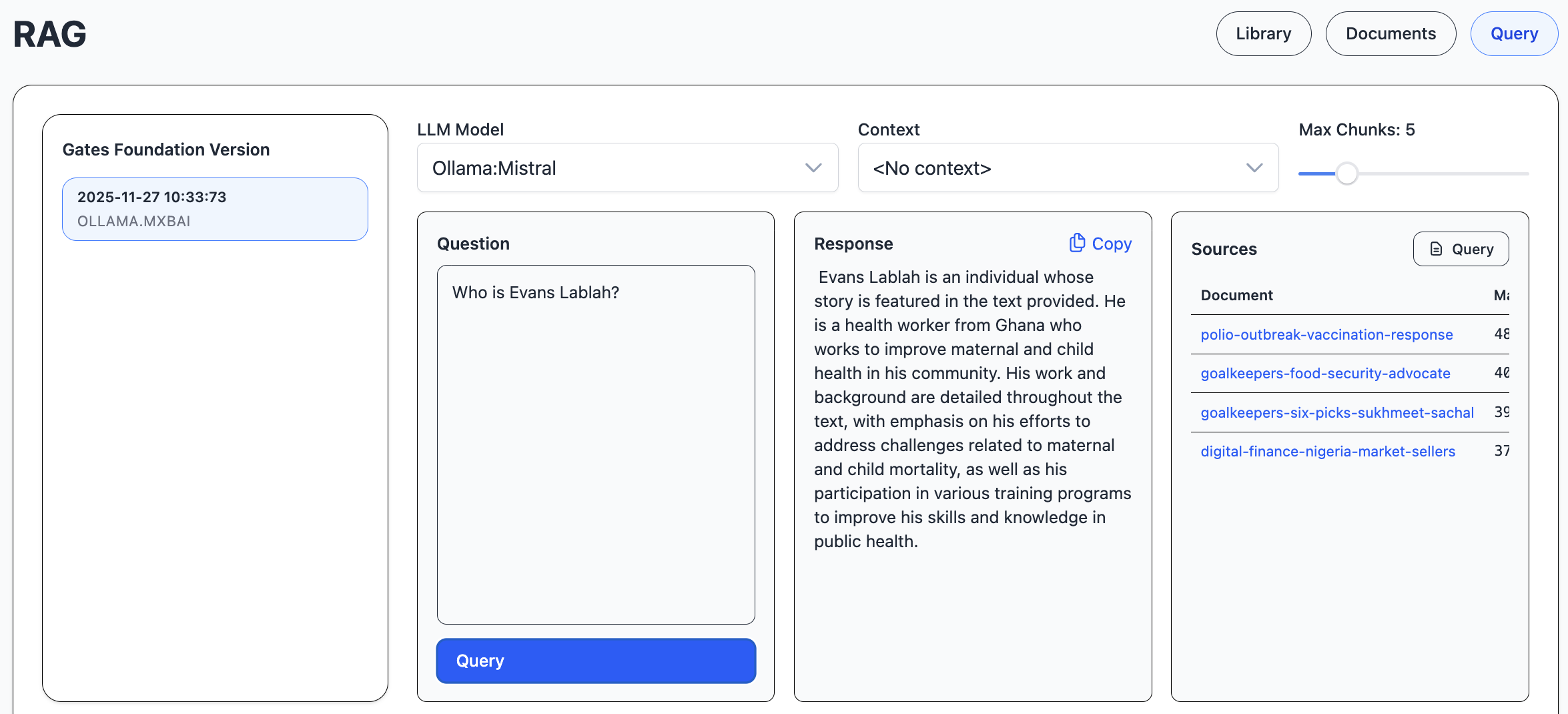
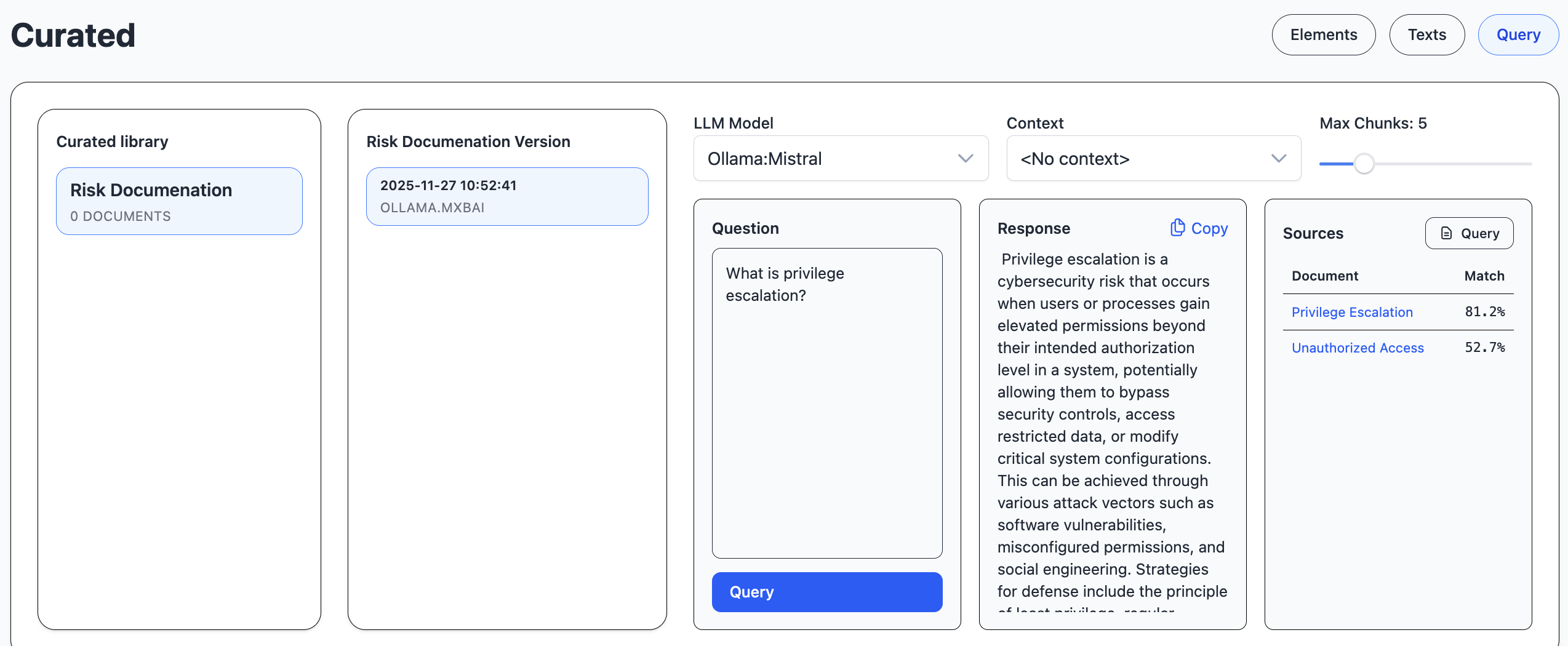
The rag module handles RAG, retrieval augmented generation. RAG is a way to find local information that resembles a question, and use a llm to summarize or search for an exact result based on the local information.
Rag documents are organized into libraries. Since all documents are encoded in the same vector database table, you can use multiple libraries in the same vector search.
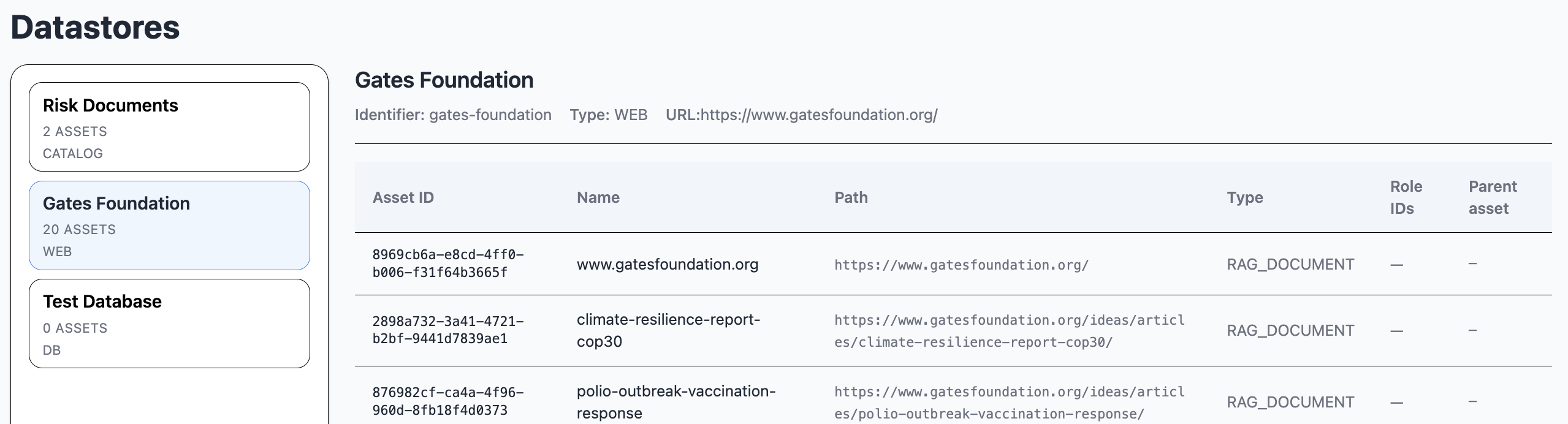
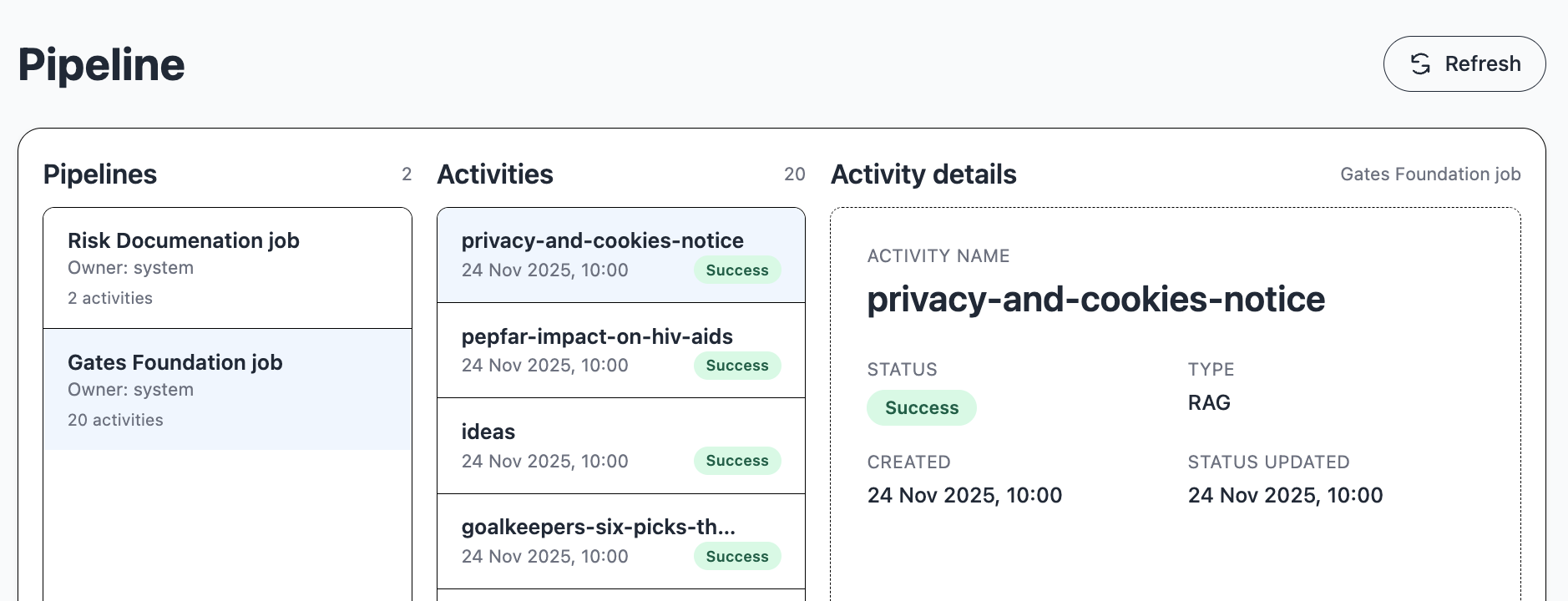
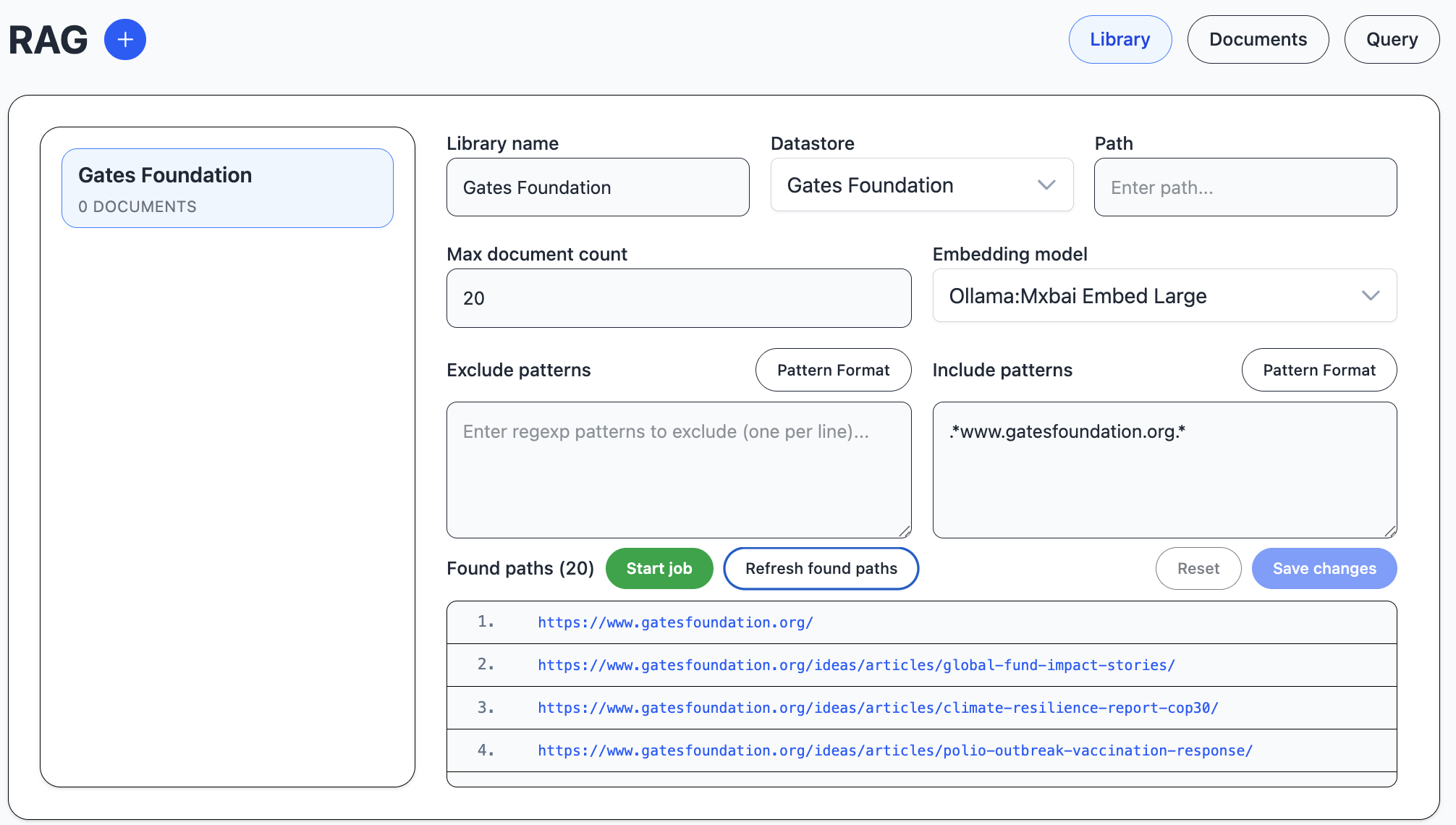
One datastore type we have added mostly for demo purposes is website.
In this image, we are scraping 20 pages from a website to find information.
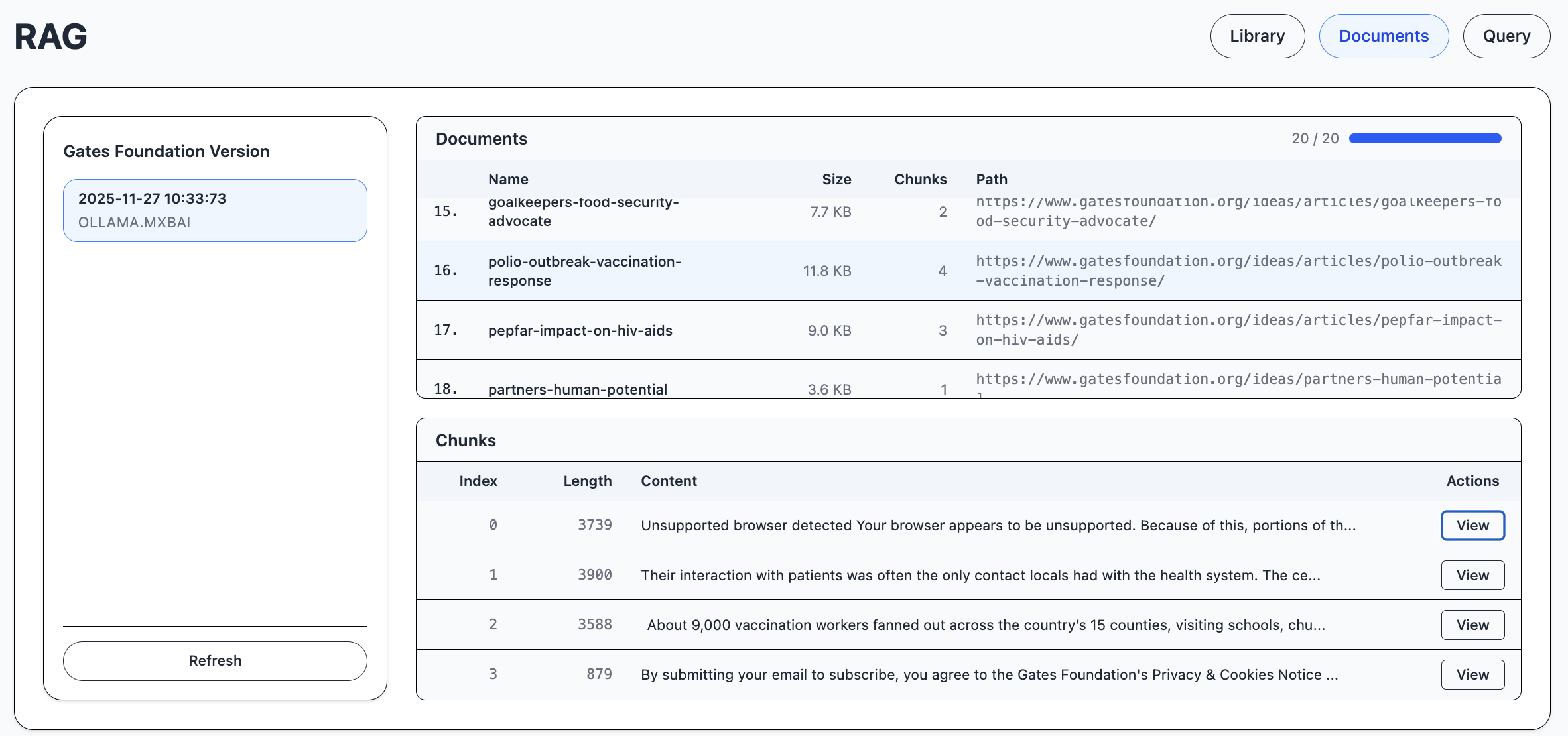
Then we start a pipeline job to download the pages, divide them into chunks
and calculate an embedding vector that represents the chunk content.
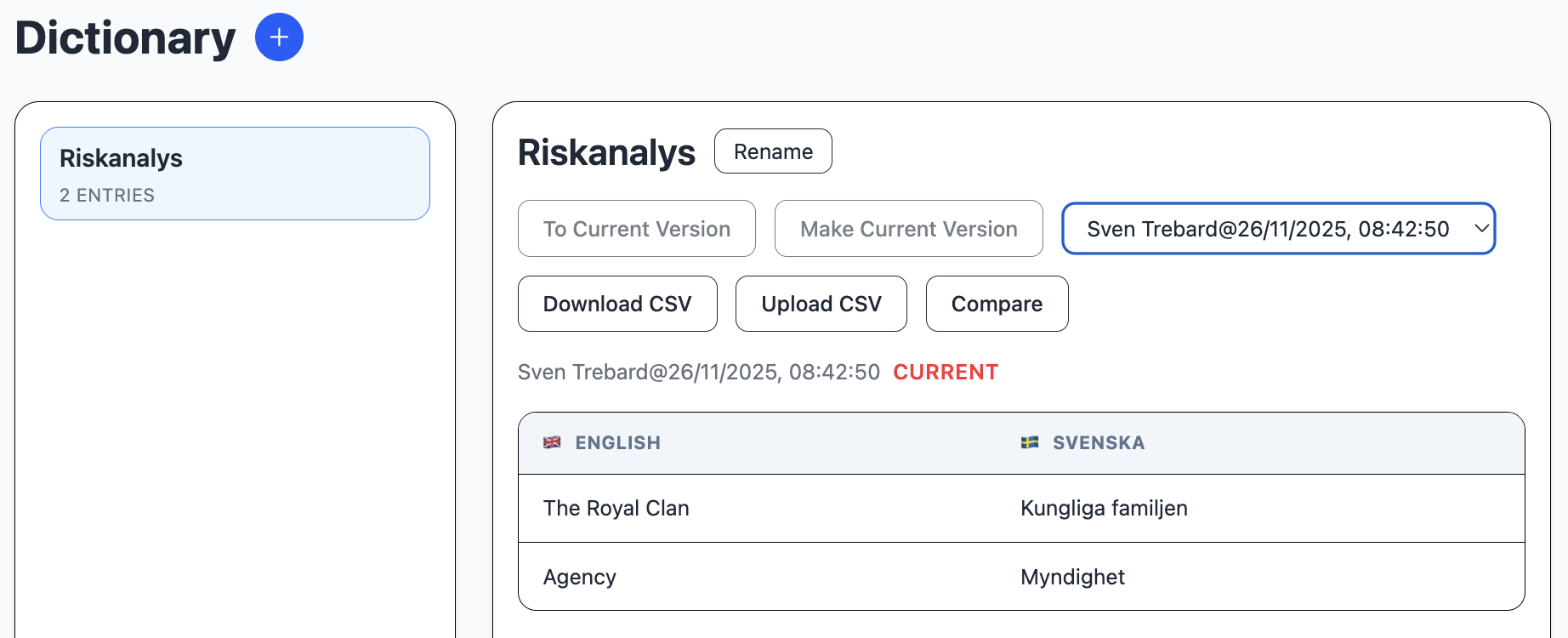
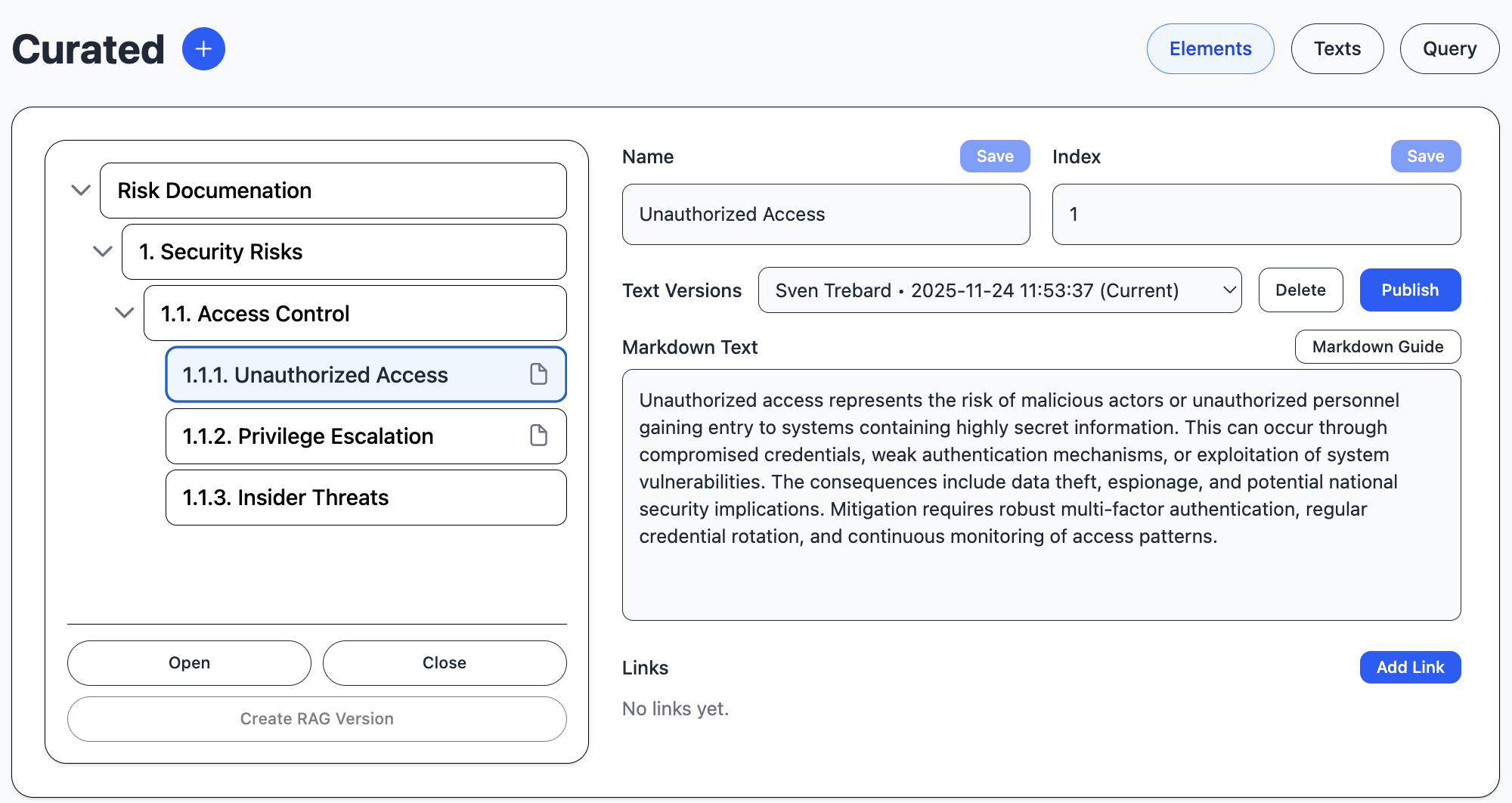
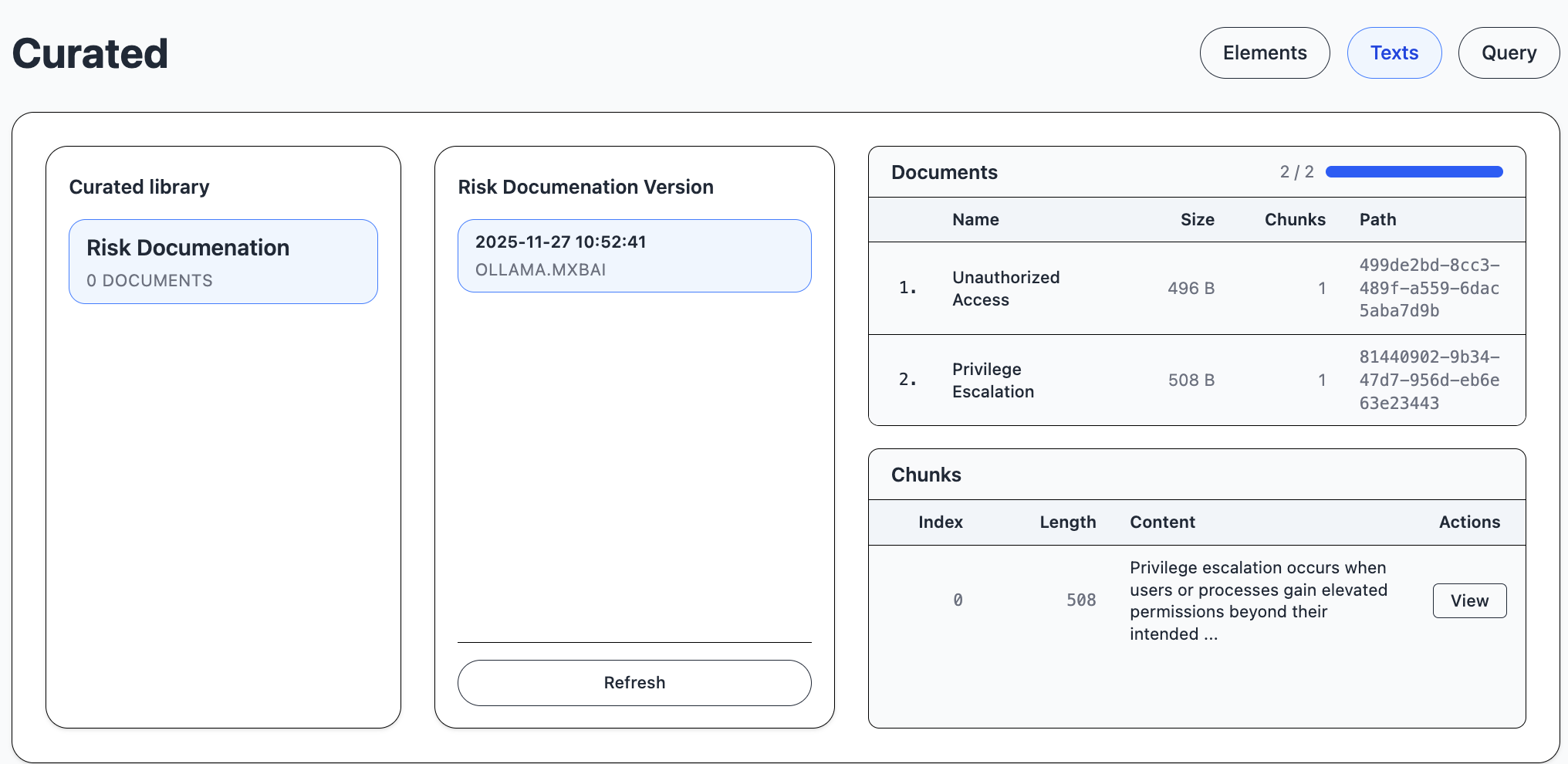
Curated
The curated module handles curated text and images to be used in standard documents. It uses RAG structure to encode and query the text, although the text can also be used in documents without modification.
The elements are divided into libraries, which are the top elements of the element tree, and a hierarchical structure of curated, versioned texts.
You select a top element and start a pipeline job to create embeddings for all texts below the top element. The embeddings are associated with a new version, so you can compare text changes.
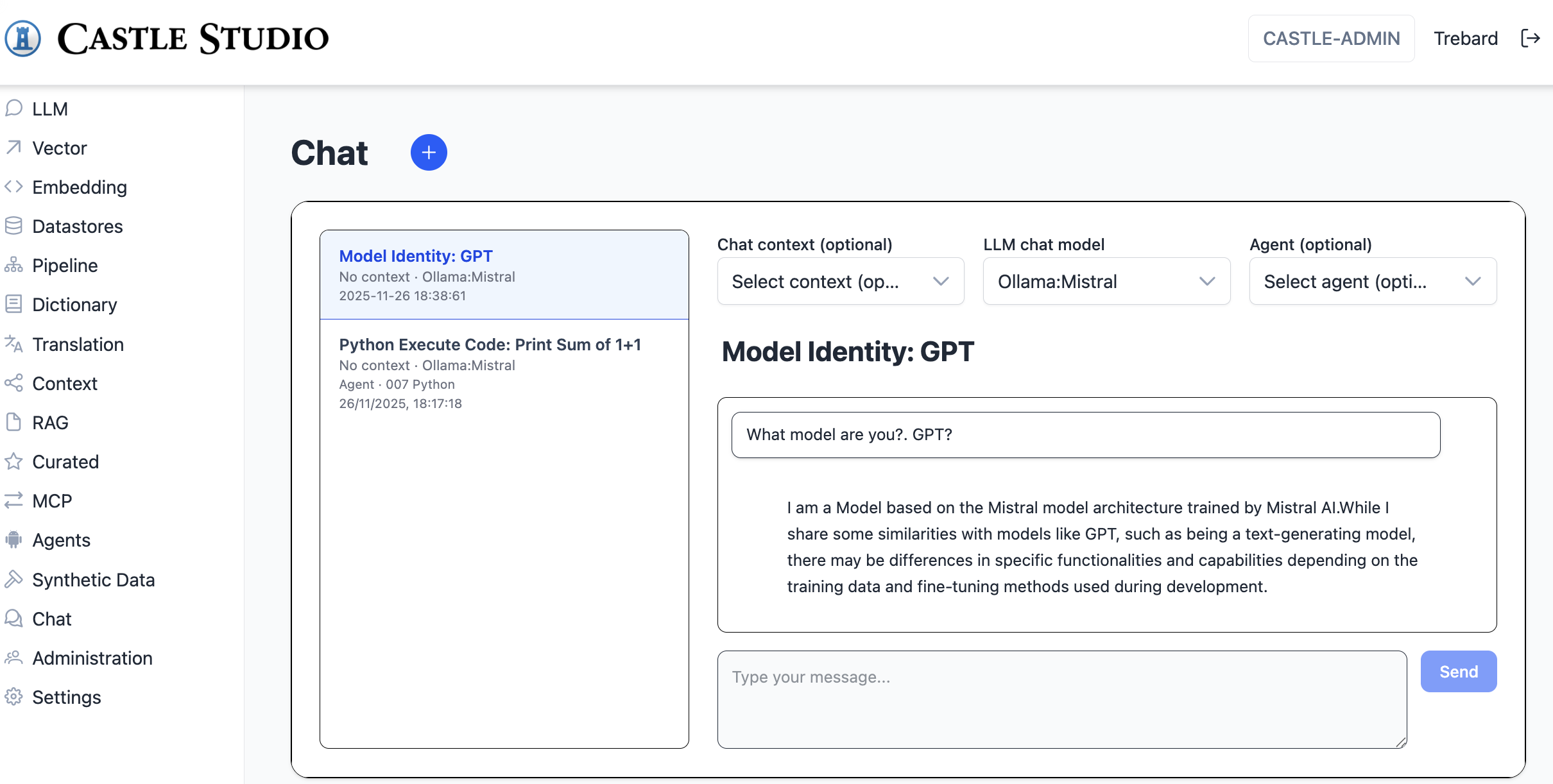
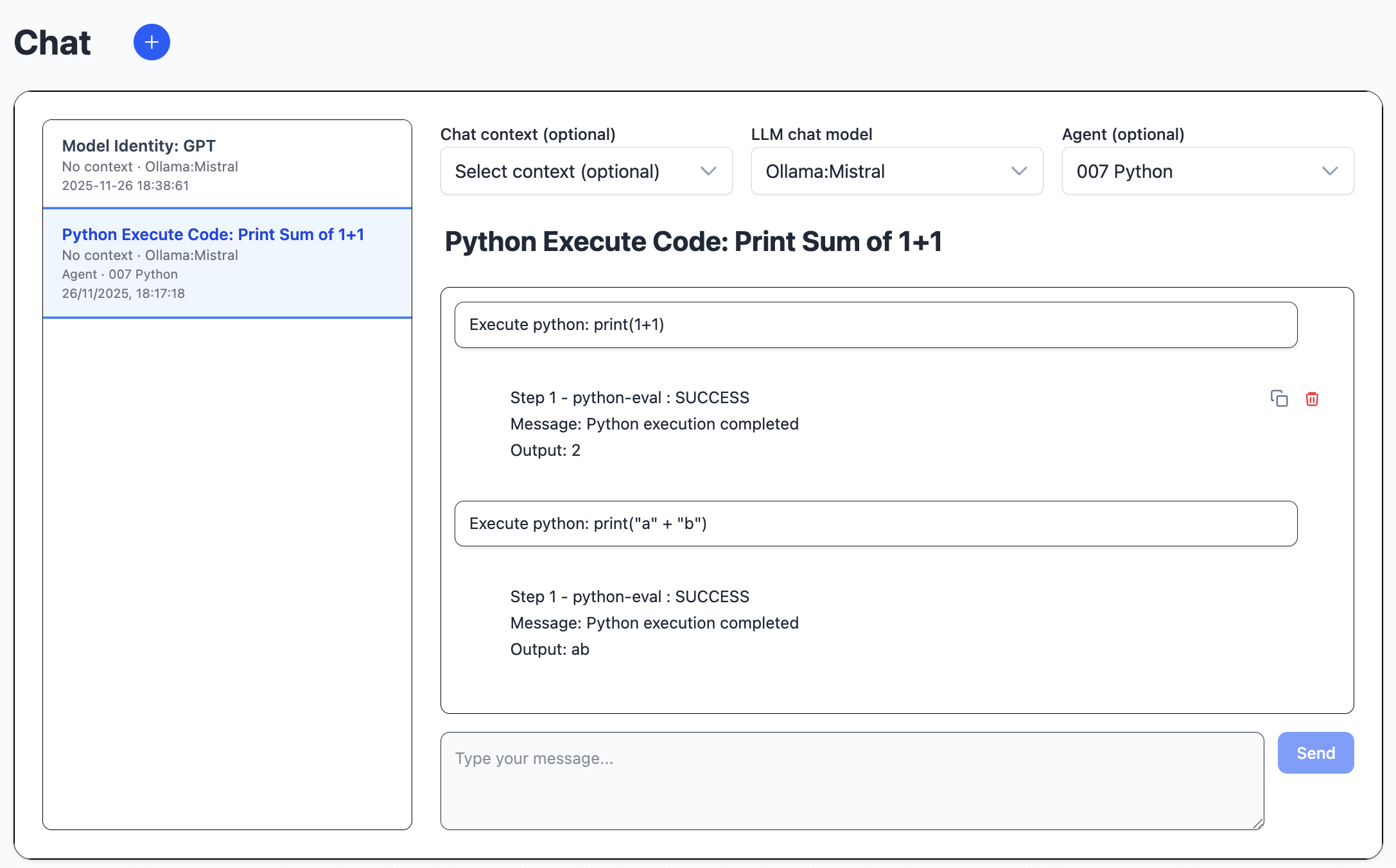
Chat
The chat module handles chat conversations.
The user types a message, and the llm streams a response.
Conversations belong to individual users. They consists of context, llm and agent selection, as well as user and assistant message history. The first user message is used to set the name of the conversation. The chat uses Spring AI chat history.
Architecture
Contact
Contact Sven Trebard.